Introduction to Heart Health and Diet
Heart health is a pivotal component of overall wellbeing, playing a fundamental role in preventing cardiovascular diseases. The heart, as a vital organ, requires proper care and attention, particularly in the context of dietary habits. Research consistently demonstrates that what we consume has a profound impact on our cardiovascular health. This connection emphasizes the importance of understanding how food choices can either nourish or compromise heart function.
Modern lifestyle practices, characterized by high-calorie, low-nutrient foods, often lead individuals down a path towards heart disease. Unhealthy diets rich in saturated fats, trans fats, sodium, and added sugars can contribute to the development of conditions such as hypertension, high cholesterol levels, and obesity. These ailments significantly increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. Therefore, recognizing and addressing poor dietary habits is crucial in promoting heart health.
To achieve and maintain cardiovascular wellness, individuals must prioritize informed nutritional decisions. A balanced diet predominantly consisting of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats has been shown to lower the risk of heart-related issues. Incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, nuts, and seeds, can further enhance heart health by reducing inflammation and improving lipid profiles.
The shift towards a heart-healthy diet not only fosters the prevention of heart disease but also enhances overall quality of life. Individuals who engage with their dietary choices are more adept at recognizing the long-term benefits of nutritional interventions. Consequently, understanding the integral relationship between diet and heart health is vital for fostering a healthier society.
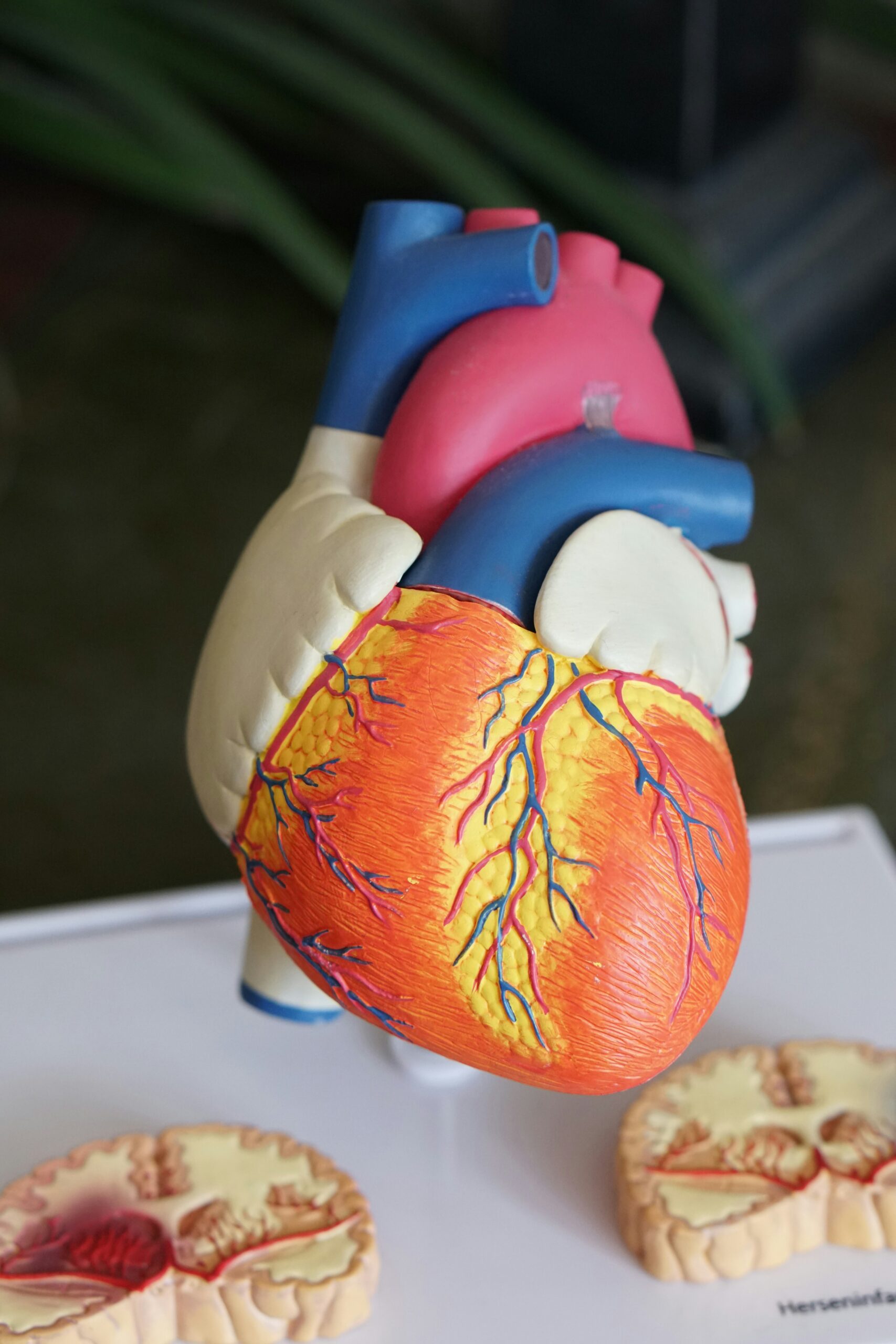
Understanding the Heart: Anatomy and Function
The heart is a remarkable organ, central to the cardiovascular system, responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It consists of four chambers: two upper atria and two lower ventricles. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body and sends it to the right ventricle, which pumps it to the lungs for oxygenation. The left atrium, receiving oxygen-rich blood from the lungs, transfers it to the left ventricle, the strongest chamber, which then distributes it to the rest of the body. This intricate process ensures that every cell receives the oxygen and nutrients necessary for optimal functioning.
Understanding the heart’s anatomy highlights its vital role in maintaining overall health. The heart operates continuously, influenced by various external and internal factors. One of the most significant influences on heart function is lifestyle, particularly dietary choices. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential for promoting cardiovascular health. Nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and antioxidants play a crucial role in reducing inflammation and maintaining healthy blood pressure levels, which are imperative for optimal heart function.
The impact of diet extends beyond just nutrient intake; it shapes the body’s overall metabolic processes. For instance, diets high in saturated fats and sugars can lead to conditions such as hypertension, high cholesterol, and obesity, which are major risk factors for heart disease. Conversely, adopting a heart-healthy diet can significantly lower these risks, promoting better heart health and increasing longevity. Therefore, an understanding of the heart’s anatomy and function underscores the importance of lifestyle factors, particularly the role of diet, in sustaining cardiovascular health.
The Impact of Diet on Heart Disease
Dietary choices play a crucial role in the development and progression of heart disease. Numerous studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between unhealthy eating patterns, characterized by high saturated fats, refined sugars, and low nutrient-dense foods, and an increased risk of cardiovascular health issues. The consumption of saturated fats, found primarily in red meats and full-fat dairy products, can elevate LDL cholesterol levels in the blood. This condition is commonly termed “bad” cholesterol, which directly contributes to the formation of plaque in arteries, eventually leading to atherosclerosis—a major factor in heart disease.
Similarly, diets that are excessive in refined sugars, often found in processed foods and sugary beverages, may significantly contribute to the risk of developing cardiovascular conditions. High sugar intake can lead to obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome, all of which are established risk factors for heart disease. Moreover, a diet low in essential nutrients, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, can further exacerbate these risks by failing to provide the necessary antioxidants, fiber, and omega-3 fatty acids that promote heart health.
Furthermore, the detrimental effects of a poor diet extend beyond immediate weight gain; they can lead to chronic inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which have been linked to heart disease. It is important to note that adopting a heart-healthy diet not only mitigates the risk factors for heart disease but also enhances overall well-being. Emphasizing the consumption of nutrient-rich foods while minimizing the intake of harmful fats and sugars has been shown to yield profound benefits for cardiovascular health.
In conclusion, recognizing the impact of diet on heart disease is essential for promoting cardiovascular health. By making conscious dietary choices, individuals can considerably reduce their risk and improve their heart health.
Heart-Healthy Foods: What to Include in Your Diet
Maintaining a heart-healthy diet is essential for preventing cardiovascular diseases and promoting overall wellness. The foods we consume significantly influence our heart health, making it vital to include specific nutrient-rich options in our daily meals. A balanced diet featuring a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can lay the foundation for a strong cardiovascular system.
Fruits and vegetables are abundant in essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which help reduce inflammation and lower blood pressure. Dark leafy greens, such as spinach and kale, are high in fiber and can be easily incorporated into salads, smoothies, or soups. Berries, including blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries, are excellent for heart health due to their high levels of antioxidants and are a delightful addition to breakfast cereals or yogurt.
Whole grains provide essential nutrients and fiber, aiding in digestion and helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Options like oatmeal, brown rice, quinoa, and whole-grain bread are excellent choices. Incorporating these grains into meals can be as simple as replacing white rice with quinoa or choosing whole-grain pasta over refined options.
Lean protein sources, such as chicken, fish, beans, and legumes, play a vital role in heart health. Fatty fish, including salmon and mackerel, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are known to support heart function and reduce cholesterol levels. Aim to include fish in your diet at least twice a week while integrating plant-based proteins like lentils and chickpeas into your meals for added fiber and nutrients.
Lastly, healthy fats found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil are crucial for heart health as they can help reduce harmful cholesterol levels. Using olive oil as a dressing for salads or as a cooking base can enhance flavor while providing beneficial monounsaturated fats. The key to a heart-healthy diet is diversity, so incorporating a variety of these food groups will not only improve heart health but also contribute to overall well-being.
Tips for Improving Your Cardiovascular Health Through Diet
Maintaining a healthy heart requires conscious dietary choices. Here are some practical tips to enhance cardiovascular health through dietary adjustments. First and foremost, meal planning is essential. By organizing your meals in advance, you can ensure a balanced intake of food that includes ample fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. It also helps in avoiding last-minute, unhealthy food choices that often compromise heart health.
Reading nutrition labels is another critical strategy. Familiarizing yourself with the nutritional information on food packaging allows you to identify unhealthy ingredients such as added sugars, sodium, and saturated fats. Pay particular attention to the serving sizes indicated on the labels, which may significantly differ from what you perceive as a standard portion. This can help you make informed decisions about what to include in your diet and maintain appropriate portion control.
Managing portion sizes is vital for maintaining a heart-healthy diet. Smaller plates and bowls can create an illusion of a fuller plate, helping to prevent overeating. Incorporating fruits and vegetables into every meal not only increases fiber intake but also creates a fulfilling meal experience. Aim to fill half of your plate with these nutrient-dense foods.
Furthermore, it is advisable to limit the consumption of processed foods, which often contain unhealthy trans fats, high levels of salt, and sugar. Instead, focus on cooking fresh meals whenever possible, as this allows you to control the ingredients and cooking methods used. Preparing meals at home can be both healthier and more cost-effective.
Overall, making thoughtful dietary modifications can significantly contribute to better cardiovascular health. By implementing these strategies and remaining mindful of your food choices, you can take proactive steps toward nourishing your heart.
Establishing Healthy Eating Habits
Developing healthy eating habits is a fundamental step towards achieving optimal cardiovascular health. A consistent and balanced diet not only helps in managing weight but also plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of heart disease. To cultivate these habits, one can start by making gradual changes rather than opting for abrupt shifts in dietary patterns. This method ensures that these modifications are sustainable and easier to incorporate into daily routines.
One effective strategy for establishing long-term healthy eating habits is to create a weekly meal plan. This plan should include a variety of heart-healthy foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. When grocery shopping, focus on purchasing whole, minimally processed foods. Reading food labels can also aid in making informed decisions, allowing individuals to avoid products high in sodium, added sugars, and unhealthy fats, which could jeopardize cardiovascular health.
Staying motivated is another critical aspect of maintaining healthy eating habits. Setting realistic, achievable goals can help individuals stay on track. For example, start by incorporating one additional serving of vegetables into daily meals or swapping out refined grains for whole grains. Celebrating these small victories reinforces the commitment to a heart-healthy diet.
Additionally, it is essential to build a supportive environment that fosters healthy eating. This could include cooking at home more often, involving family members in meal preparation, or even sharing healthy recipes with friends. Social support can be incredibly beneficial for maintaining motivation and encouraging adherence to a balanced diet. Educating oneself about nutrition can also empower individuals to make informed choices that prioritize cardiovascular health.
Finally, consistency is key. While occasional indulgences are perfectly acceptable, the emphasis should remain on a balanced diet. By integrating these practices into everyday life, individuals can develop healthy eating habits that significantly contribute to long-lasting heart health.
The Role of Physical Activity in Heart Health
Physical activity plays an essential role in maintaining cardiovascular health, complementing the nutritional benefits derived from a heart-healthy diet. Engaging in regular exercise can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease, lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and enhance overall well-being. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that adults engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week. This can include activities such as brisk walking, running, cycling, swimming, or dancing.
The benefits of physical activity for heart health are numerous. First, exercise helps to strengthen the heart muscle, allowing it to pump blood more efficiently throughout the body. Additionally, regular physical activity aids in weight management, which is crucial for preventing obesity-related heart issues. Furthermore, exercise promotes better blood circulation, which works in tandem with a balanced diet to ensure that nutrients are effectively delivered to the heart and other body organs.
Incorporating physical activity into daily routines does not have to be daunting. Simple lifestyle changes can make a significant difference. For instance, opting to take the stairs instead of the elevator, walking or cycling instead of driving for shorter distances, or engaging in active hobbies such as gardening or playing sports can all contribute to increased physical activity levels. Group fitness classes or activities with friends and family can also make exercising more enjoyable and sustainable. By making these conscious efforts, individuals can create an environment that fosters heart health and enhances the benefits derived from their dietary choices.
In conclusion, while a heart-healthy diet is fundamental to cardiovascular well-being, the incorporation of regular physical activity serves as a vital complement. Together, a balanced diet and a robust exercise regimen form the cornerstone of a heart-healthy lifestyle, promoting longevity and improving quality of life.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals for Personalized Advice
In navigating the complex relationship between diet and cardiovascular health, consulting healthcare professionals is paramount. Dietitians, nutritionists, and physicians play crucial roles in formulating personalized nutrition plans that cater to individual health needs, significantly contributing to heart health management and disease prevention. These experts bring a wealth of knowledge on how dietary choices impact cardiovascular function, providing evidence-based recommendations tailored to each person’s unique situation.
For individuals who may already have existing heart conditions, personalized advice from these professionals is particularly vital. Such conditions, including hypertension, dyslipidemia, or heart failure, may require specific dietary modifications not only to improve symptoms but also to mitigate the risk of future complications. Healthcare professionals can carry out detailed assessments, factoring in essential elements such as age, weight, lifestyle, and any underlying medical issues, leading to more effective and sustainable dietary adjustments.
Moreover, healthcare professionals can help debunk common nutritional myths that may mislead individuals. The dynamic nature of nutrition science underscores the importance of professional guidance to ensure that individuals are not only adhering to dietary recommendations but also understanding the rationale behind them. This holistic approach facilitates better compliance and fosters a greater appreciation for the role that food choices play in maintaining cardiovascular health.
Ultimately, incorporating the insights of healthcare providers can empower individuals to take control of their heart health. Through regular consultations and follow-ups, they can track progress and make necessary adjustments to their nutrition plans. This ongoing support is essential for anyone seeking to prevent heart disease or manage existing conditions effectively, emphasizing that a proactive approach towards dietary choices is critical in promoting overall heart health.
Conclusion: Embracing a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining optimal cardiovascular health is fundamentally linked to the dietary choices we make daily. A heart-healthy lifestyle necessitates a proactive approach to nutrition, emphasizing foods rich in essential nutrients that support heart function, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. These food groups not only aid in reducing cholesterol levels and managing blood pressure but also play a pivotal role in preventing chronic diseases associated with cardiovascular conditions.
Furthermore, understanding the importance of portion control and limiting processed and high-sugar foods cannot be overemphasized. Individuals are encouraged to be vigilant about intuitive eating, which focuses on recognizing hunger cues and fostering a positive relationship with food. This practice can help mitigate overeating, ultimately contributing to better heart health. Moreover, incorporating a variety of foods can ensure that the body receives a balanced intake of vital nutrients necessary for optimal cardiovascular function.
In addition to dietary modifications, embracing regular physical activity is equally important for maintaining heart health. Engaging in moderate exercise several times a week can significantly improve cardiovascular function, facilitate weight management, and enhance overall well-being. Pairing a nutritious diet with physical activity not only optimizes heart function but also cultivates a lifestyle that contributes to longevity and quality of life.
Ultimately, making informed food choices and committing to regular exercise creates a strong foundation for a heart-healthy lifestyle. Each small decision contributes to a larger impact on personal health and well-being. By focusing on these areas, individuals can take meaningful steps toward improving their cardiovascular health and nourishing their hearts effectively.
